2 minutes
go_zero的API签名验证
背景
最近在使用go_zero框架的时候,想给api加一个签名,但是搜索了一下,没有发现很完整的教程,所以在这里记录一下。最开始通过一些博客加了一下签名,在框架验签的时候,发现签名失败,所以我们从验签开始往回推。
go_zero验签
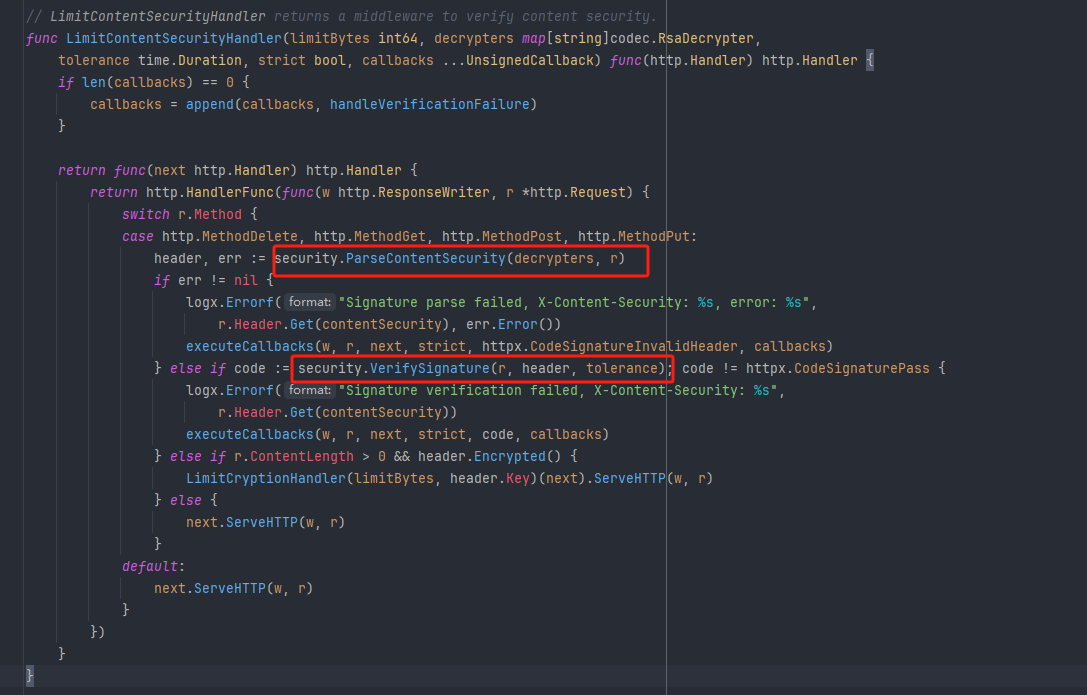
我们从这两个方法讲起来
ParseContentSecurity
func ParseContentSecurity(decrypters map[string]codec.RsaDecrypter, r *http.Request) (
*ContentSecurityHeader, error) {
// 获取请求头中的X-Content-Security字段
contentSecurity := r.Header.Get(httpx.ContentSecurity) //X-Content-Security
attrs := httpx.ParseHeader(contentSecurity)
// 获取请求头中的X-Content-Security字段中的key、secret、signature字段
fingerprint := attrs[httpx.KeyField] //"key"
secret := attrs[httpx.SecretField] //"secret"
signature := attrs[signatureField] //"signatur"
if len(fingerprint) == 0 || len(secret) == 0 || len(signature) == 0 {
return nil, ErrInvalidHeader
}
decrypter, ok := decrypters[fingerprint]
if !ok {
return nil, ErrInvalidPublicKey
}
// 解密secret
decryptedSecret, err := decrypter.DecryptBase64(secret)
if err != nil {
return nil, ErrInvalidSecret
}
//在secret中获取时间戳和类型和key
attrs = httpx.ParseHeader(string(decryptedSecret))
base64Key := attrs[httpx.KeyField] //key
timestamp := attrs[timeField] //时间戳
contentType := attrs[httpx.TypeField] //类型
// 使用base64解密,在使用私钥解密
key, err := base64.StdEncoding.DecodeString(base64Key)
if err != nil {
return nil, ErrInvalidKey
}
cType, err := strconv.Atoi(contentType)
if err != nil {
return nil, ErrInvalidContentType
}
return &ContentSecurityHeader{
Key: key,
Timestamp: timestamp,
ContentType: cType,
Signature: signature,
}, nil
}
在这个方法里面我们可以看到,header里面的参数,这里是分号结尾,可以在ParseHeader方法里面看到
- X-Content-Security: key=xxx;secret=xxx;signature=xxx
- 使用base64解密,在使用私钥解密secret,已经获取到了type,time,加密的key ,再通过base64解密获取key的值
VerifySignature验签方法
func VerifySignature(r *http.Request, securityHeader *ContentSecurityHeader, tolerance time.Duration) int {
seconds, err := strconv.ParseInt(securityHeader.Timestamp, 10, 64)
if err != nil {
return httpx.CodeSignatureInvalidHeader
}
now := time.Now().Unix()
toleranceSeconds := int64(tolerance.Seconds())
if seconds+toleranceSeconds < now || now+toleranceSeconds < seconds {
return httpx.CodeSignatureWrongTime
}
reqPath, reqQuery := getPathQuery(r)
signContent := strings.Join([]string{
//时间戳
securityHeader.Timestamp,
//请求方法
r.Method,
//请求路径
reqPath,
//请求参数
reqQuery,
//使用散列算法生成body的hash值
computeBodySignature(r),
}, "\n")
//使用进行sha256加密,在用base64加密
actualSignature := codec.HmacBase64(securityHeader.Key, signContent)
//生成的签名和原始签名对比
if securityHeader.Signature == actualSignature {
return httpx.CodeSignaturePass
}
logx.Infof("signature different, expect: %s, actual: %s",
securityHeader.Signature, actualSignature)
return httpx.CodeSignatureInvalidToken
}
- 加密的内容
- 时间戳
- 请求方法
- 请求路径
- 请求参数
- 请求体hash值
- 对内容进行sha256.New(key) 加密,在用base64加密
签名算法
请参考这篇文章
签名请求案例
配置文件
Signature:
Strict: true # 是否开启校验,调试的时候可以关掉,默认是关闭
Expiry: 24h # 签名字段的过期时间,默认 1 h
PrivateKeys: # 密钥以及指纹,密钥是上面 RSA 文件位置,指纹自定义,可以多组
- Fingerprint: "aabb"
KeyFile: E:\go_project\ai_headset_api\etc\private.pem
请求
type UpdateTodoAlarmReq struct {
Id int64 `json:"id"`
AlarmStatus int `json:"alarmStatus"`
}
func TestRequest(t *testing.T) {
key1 := "aabb"
pub_key := "-----BEGIN RSA PUBLIC KEY-----\nMIIBIjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAAOCAQ8AMIIBCgKCAQEAzCbcSJ2Wo5QGmTEpBkKI\nb6lqjRpmSbOfNIYsT/J3u9t4PbCcWYDRyoybuOlWbYQqpzdEvnMm8bCO1m2vUmPL\n6gUVi6uz3RTn+yOQEhRFqu5YFzvPqrSl0SYOwP1NdSzO9te1Kb2DtmlLQExbhan2\n4jcwIjwSogtpoC6ymVYzHjGDare6j5cMqBDGewHwUU2p6yxOkwbLn0ZLVYGBWolQ\nzc8hV3BK01ENnimDhkRFpxs2HDEQlBKfDpqo77JKyzvUnYmSu/xN8vcNqzHb5Ral\nKI8Xep8caRh5+l1ah78nGdvvJ1YX1FEjctGm8iMNI12rw79agdFYJIPoBFvPreUJ\nwQIDAQAB\n-----END RSA PUBLIC KEY-----\n"
now := time.Now().Unix()
req := UpdateTodoAlarmReq{
Id: 1,
AlarmStatus: 1,
}
marshal, err := json.Marshal(req)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
request, err := http.NewRequest("PUT", "http://127.0.0.1:8888/v1/update_todo_alarm", bytes.NewBuffer(marshal))
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
request.Header.Set("Content-Type", "application/json")
request.Header.Set("Authorization", "Bearer eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJleHAiOjE3MTc0Mzg1MzcsImlhdCI6MTcxNzQwMjUzNywidWlkIjoxfQ.dPL3JkQdIMr183cOZ2o6BAcZYm53GJnwIRgAvCoKTeg")
content := strings.Join([]string{
fmt.Sprintf("type=%d", 0),
fmt.Sprintf("key=%s", base64.StdEncoding.EncodeToString([]byte(key1))), //对私钥密码做base64加密
fmt.Sprintf("time=%s", strconv.FormatInt(now, 10)),
}, "; ")
//用公钥对所得字符串进行rsa加密取base64值
encrypter, _ := codec.NewRsaEncrypter([]byte(pub_key))
output, _ := encrypter.Encrypt([]byte(content))
secret := base64.StdEncoding.EncodeToString(output)
str := strings.Join([]string{
strconv.FormatInt(now, 10),
request.Method,
request.URL.Path,
"",
computeBodySignature(string(marshal)),
}, "\n")
t.Log(str)
t.Log("body hash: ", computeBodySignature(string(marshal)))
request.Header.Set("X-Content-Security", strings.Join([]string{
fmt.Sprintf("key=%s", key1),
fmt.Sprintf("secret=%s", secret),
fmt.Sprintf("signature=%s", codec.HmacBase64([]byte(key1), str)),
}, "; "))
t.Log("Hmacse64: ", codec.HmacBase64([]byte(key1), str))
client := http.Client{}
do, err := client.Do(request)
fmt.Println(do, err)
}
func computeBodySignature(body string) string {
sha := sha256.New()
io.WriteString(sha, body)
return fmt.Sprintf("%x", sha.Sum(nil))
}